Home » Sustainable Packaging Options for the Pet Industry
Sustainable Packaging Options for the Pet Industry

Sustainability in pet product packaging involves balancing environmental impact with functional performance. Materials must protect against moisture, oxygen, and pests while also meeting recyclability or compostability goals. Choosing the right approach requires a clear understanding of available technologies, regulatory compliance, and supply chain realities.
Recyclable Mono-Material Films
- Description: Flexible packaging made from a single resin type (e.g., all-PE or all-PP).
- Benefits:
- Compatible with store drop-off or curbside programs in certain municipalities.
- Eliminates the separation challenges of multi-material laminates.
- Limitations:
- Lower barrier properties compared to foil or metallized films unless enhanced with coatings.
- May require thicker gauges for equivalent performance.
Post-Consumer Recycled (PCR) Content
- Description: Packaging that incorporates recycled resin from consumer waste streams.
- Benefits:
- Reduces reliance on virgin plastic.
- Demonstrates brand commitment to circular economy principles.
- Limitations:
- Variability in resin quality can impact clarity, seal strength, and barrier.
- Regulatory restrictions for direct food contact in some markets.
Compostable Films
- Description: Materials derived from plant-based sources (e.g., PLA, starch blends) designed to break down in industrial composting conditions.
- Benefits:
- Reduces landfill waste when properly disposed.
- Appeals to eco-conscious consumers.
- Limitations:
- Requires access to industrial composting facilities (rare in many regions).
- Lower mechanical strength and shorter shelf life than conventional films.
Paper-Based Pet Food Packaging
- Description: Multiwall kraft paper bags with or without barrier liners.
- Benefits:
- Widely recyclable in paper streams when unlined.
- Strong consumer perception of sustainability.
- Limitations:
- Requires additional barrier layer for moisture or grease resistance.
- Lower tear resistance than woven poly or laminated film.

Bio-Based Plastics
- Description: Plastics derived from renewable biomass sources such as sugarcane ethanol-based PE.
- Benefits:
- Reduces carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based resins.
- Matches performance of conventional PE in many applications.
- Limitations:
- Availability and cost can be volatile.
- Does not inherently solve end-of-life recycling challenges.
Performance and Testing Considerations
- Barrier Testing: ASTM F1249 for WVTR and ASTM D3985 for OTR confirm material suitability.
- Seal Strength: ASTM F88/F88M ensures structural integrity.
- Life-Cycle Analysis (LCA): Quantifies environmental trade-offs of each packaging option.
References
ASTM International. (2013). ASTM F1249-13: Standard test method for water vapor transmission rate through plastic film and sheeting using a modulated infrared sensor. ASTM International. https://doi.org/10.1520/F1249-13
ASTM International. (2010). ASTM D3985-10: Standard test method for oxygen gas transmission rate through plastic film and sheeting using a coulometric sensor. ASTM International. https://doi.org/10.1520/D3985-10
Sustainable Packaging Coalition. (2023). Sustainable materials and design strategies. https://sustainablepackaging.org
Supplier contracts can make or break a packaging program. Without the right terms, buyers risk price volatility, missed lead times, and inconsistent product quality. In 2026, negotiating smart contracts is
Packaging compliance is no longer optional—it’s a requirement for accessing retail shelves, shipping networks, and international markets. In 2026, buyers must navigate evolving regulations around sustainability, labeling, and testing to
In 2026, sustainability is no longer just a trend—it’s a buyer expectation. Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification has become a key benchmark for responsible packaging, signaling that materials are sourced
Sustainability is now a top priority for packaging buyers. Retailers, regulators, and consumers are all demanding packaging solutions that reduce environmental impact without sacrificing performance. In 2026, buyers must balance
Home » Sustainable Packaging Options for the Pet Industry
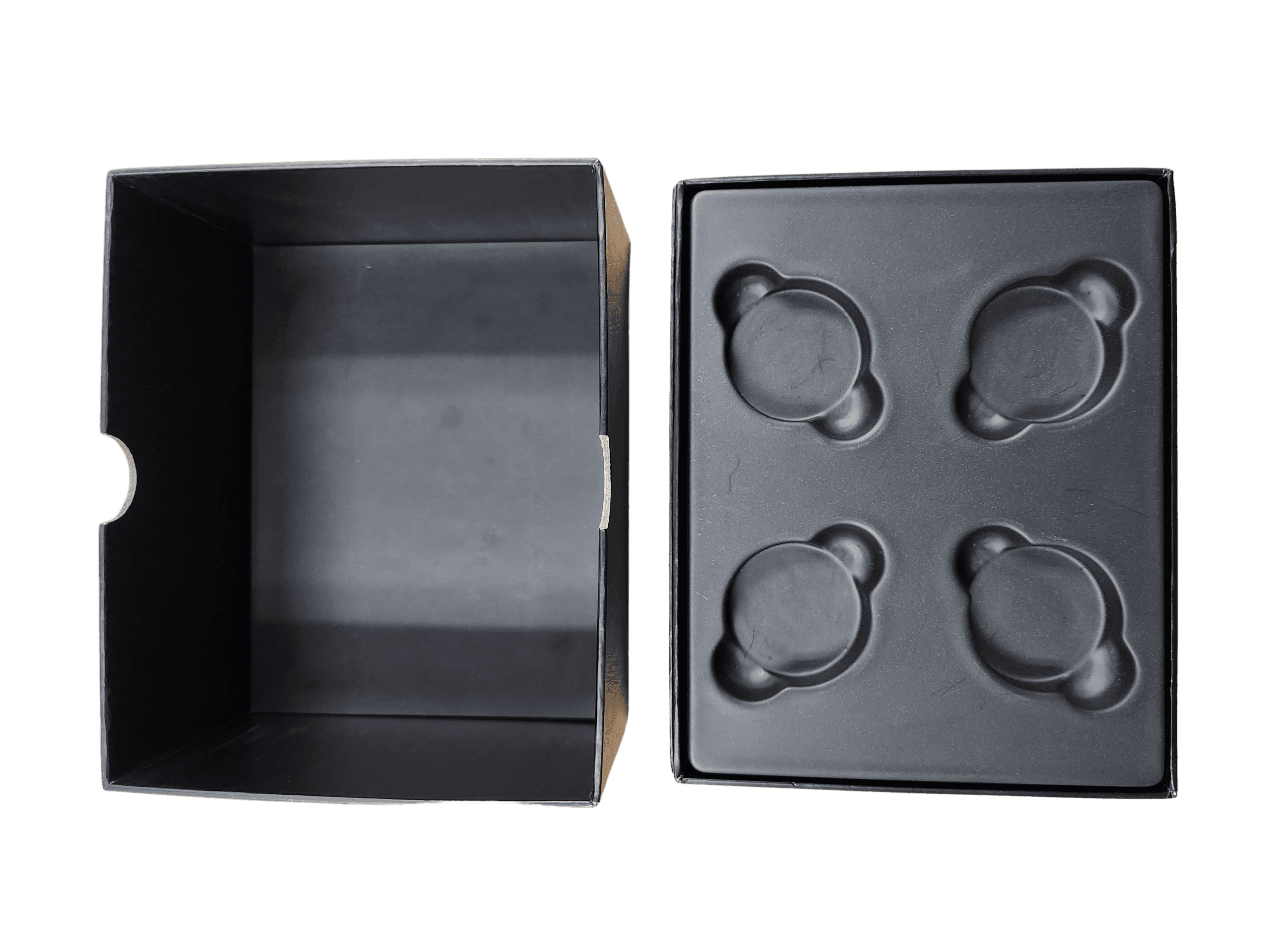

High Impact Polystyrene, commonly known as HIPS, is a versatile and widely used thermoplastic renowned for its unique blend of properties. This material is crucial in various industries, including consumer goods and packaging, due to its high-impact strength, rigidity, affordability, and ease of processing. Essential Properties of HIPS HIPS boasts several properties that make it an excellent choice for numerous applications: High Impact Strength: Provides durability and resistance to physical impacts. Rigidity: Maintains shape and structural integrity under stress. Chemical Resistance: Withstands exposure to many chemicals, oils, and greases. Biological Resistance: Resists degradation from biological factors like fungi and bacteria. Water Resistance: Impermeable qualities make it suitable for applications requiring moisture resistance. Fatigue Resistance: Capable of enduring repeated stress without losing its form, ideal for components like living hinges. Thermal Insulation: Offers significant insulation properties, beneficial in both industrial and consumer products. Electrical Insulation: Highly resistant to electricity, making it safe for use in electronic components. Affordability and Recyclability: Cost-effective and fully recyclable, supporting environmental sustainability. Diverse Applications of HIPS HIPS’s versatility allows its use across various sectors: Consumer Goods: Utilized in products requiring durability and impact resistance, such as toys, household appliances, and office supplies. Packaging Materials: Ideal for making clamshell containers, blister packs, and trays due to its moldability and cost-effectiveness. Automotive Industry: Used in components like interior trim parts, instrument panels, and exterior body parts due to its lightweight and sturdy nature. Construction Industry: Forms part of materials such as wall panels, ceiling tiles, and insulation boards, thanks to its insulation properties. Medical Industry: Common in the production of medical devices and packaging, valued for its chemical resistance and stability. Manufacturing Process of HIPS The production of HIPS involves several steps: Polymerization: Styrene monomers are polymerized using catalysts like benzoyl peroxide to form the HIPS polymer. Mixing: The polymer is blended with impact modifiers, stabilizers, and pigments to enhance its properties and appearance. Molding: HIPS can be shaped through extrusion or injection molding, allowing it to be formed into various products. Cooling and Finishing: Post-molding, HIPS is cooled and can undergo additional processing like trimming and polishing to achieve the desired quality. Environmental Considerations While HIPS is not biodegradable, it is recyclable. Recycling HIPS contributes to waste reduction and resource conservation, mitigating the environmental impact associated with plastic production. Frequently Asked Questions About HIPS Is HIPS food safe? Yes, when certified, HIPS is safe for food contact applications. Difference between HIPS and ABS? ABS is generally more robust with better temperature resistance, but HIPS is more cost-effective. Can HIPS be painted or printed on? Yes, HIPS can be easily painted or printed on, provided the surface is properly prepared. Color options for HIPS? Available in a broad spectrum of colors, including custom shades to meet specific project requirements. Conclusion High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) stands out as a valuable material in the realm of plastics due to its excellent properties and wide range of applications. From packaging and automotive parts to household items and medical devices, HIPS continues to be a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking a reliable, cost-effective, and versatile material. As the industry advances, the sustainability and recyclability of HIPS make it even more significant in our ongoing journey towards environmental consciousness. For further details or inquiries about using HIPS for your packaging and manufacturing needs, please contact Brown Packaging. We are committed to delivering high-quality, sustainable packaging solutions tailored to your specifications. (714)300-0650 request@brownpackaging.com Most Recent Posts: Subscribe To Our Newsletter By submitting your information, you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy. Thermoform Packaging Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Relevant Posts
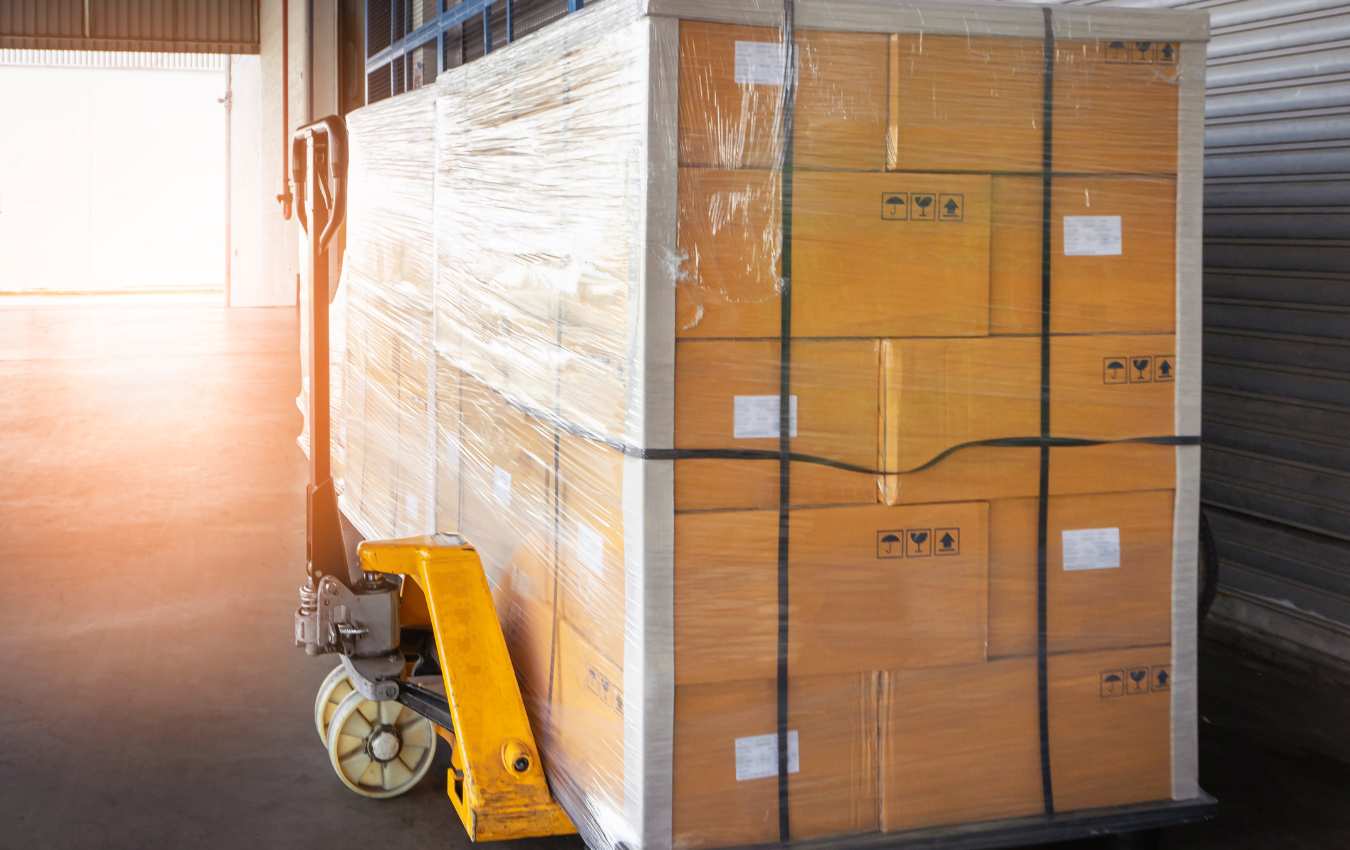

When you ship items, you run the risk of damaging them during transit. Even with careful handling, packages can bump into each other and sustain damage. That’s why it’s crucial to take measures to protect your packages during shipping. One of the easiest and most effective ways to do this is by using corrugated edge protectors. Corrugated edge protectors add an extra layer of protection to the edges and corners of your packages, preventing them from getting damaged during shipping. In addition to using edge protectors, you can also choose to use stretch film to further secure your package and prevent damage. While stretch film is optional, it can be especially useful for packages with irregular shapes or multiple items. 7 Steps to Using Corrugated Edge Protectors In this guide, we’ll take you through the steps of using corrugated edge protectors, with the option of using stretch film, to protect your packages during shipping. Step 1: Determine the size of the edge protectors you need The first step in using corrugated edge protectors is to measure the item you’re shipping. Determine the length, width, and thickness of the packaging material you’ll be using. You’ll need to choose edge protectors that are slightly larger than the item to ensure adequate protection. Additionally, consider the weight and fragility of the item. Heavier items may require thicker edge protectors, while fragile items may need extra padding or cushioning. Step 2: Choose the right type of edge protector There are several types of edge protectors to choose from, including L-shaped, U-shaped, and C-shaped protectors. L-shaped protectors are best for protecting corners, while U-shaped protectors are designed to wrap around the edge of an item. C-shaped protectors are ideal for cylindrical items like pipes or tubes. You’ll also need to choose the right material for the edge protectors. Cardboard, plastic, and foam are common options. Each material has its own strengths and weaknesses, so choose the one that best suits your needs. Step 3: Cut the edge protectors to size Use a utility knife or box cutter to cut the edge protectors to the appropriate size. Cut them long enough to cover the entire edge or corner of the item, and wide enough to provide adequate protection. For L-shaped protectors, cut the corner at a 45-degree angle to ensure a snug fit. U-shaped protectors should be cut at a 90-degree angle. Step 4: Secure the edge protectors to the item Use tape or adhesive to secure the edge protectors to the cardboard or other packaging material. Apply the tape or adhesive to both the edge protector and the packaging material to ensure a secure hold. Make sure the edge protectors are properly aligned to provide adequate protection. Step 5: Add additional protection if needed For fragile items or those with irregular shapes, consider adding additional protection. Bubble wrap, packing peanuts, or other protective materials can help cushion the item and prevent damage during shipping. If you choose to use stretch film, wrap it tightly around the package, ensuring that it’s snug but not so tight that it damages the package or its contents. Choose the appropriate type of stretch film for your specific needs, as different types have varying levels of strength and stretchability. Step 6: Label and ship the package Label your package with any necessary shipping information, such as the destination address and tracking number. Add a “Fragile” or “Handle with Care” label if necessary. Use a permanent marker or label maker to create clear, legible labels and place them in a visible location on the package. Step 7: Monitor the shipment Keep track of the shipment by utilizing the tracking information provided by the carrier. Regularly check the status and location of your package to ensure its progressing smoothly towards its destination. If you encounter any delays or issues during the shipment, promptly contact the carrier to address the problem. In cases of damaged or lost items, you may need to file a claim with the carrier to seek compensation or resolution. Summary: Edge Protectors By following these steps, you can effectively protect your packages during shipping using corrugated edge protectors and optional stretch film. Start by measuring your item and selecting the appropriate size and type of edge protectors. Cut them to size and securely attach them to your package. If necessary, add extra protection such as bubble wrap. Optionally, wrap the package with stretch film for added security, particularly for irregularly shaped or multiple-item packages. Properly label the package and monitor the shipment using tracking information. Remember, taking the time to properly protect your packages will help minimize the risk of damage during shipping. Whether you’re sending fragile items or packages with irregular shapes, using corrugated edge protectors and optional stretch film will provide an extra layer of protection and peace of mind. Happy shipping! If you are interested in edge protectors or corner boards, then partner with Brown Packaging today to get started. (714)300-0650 request@brownpackaging.com Most Recent Posts: Categories: Corrugated Ecommerce ESD Design Display Flexible Packaging Foam Folding Carton Packaging Plastic Packaging Pouch Printing Protection Retail Rigid Box Thermoform Sustainability Subscribe To Our Newsletter By submitting your information, you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy. Custom Edge Protectors Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Relevant Posts
Thermoform inserts are a versatile and essential component in various industrial and consumer applications. They are produced through a process called thermoforming, where a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable forming temperature, formed to a specific shape in a mold, and trimmed to create a usable product. In this blog, we’ll delve into the properties, applications, and other relevant aspects of thermoform inserts. Properties of Thermoform Inserts Material Flexibility: Thermoform inserts can be made from a wide range of plastics, including like PVC, PET and HIPS. Each material offers different characteristics like rigidity, clarity, and resistance to impact and chemicals. Durability: These inserts are known for their strength and durability. They can withstand significant impact and are resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for protective purposes. Lightweight: Despite their strength, thermoform inserts are relatively lightweight, which is beneficial for reducing shipping and handling costs. Customizability: The thermoforming process allows for high levels of customization. Inserts can be formed into virtually any shape and size, accommodating a wide range of products. Aesthetic Appeal: Thermoform inserts can have smooth or textured surfaces, and can be transparent or colored. This makes them visually appealing and suitable for display purposes. Applications of Thermoform Inserts Packaging Solutions: One of the most common uses of thermoform inserts is in product packaging. They are used to securely hold products in place, often seen in the packaging of electronics, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Medical Industry: In the medical field, thermoform inserts are used for packaging sterile medical devices and equipment due to their ability to be sterilized and their contaminant-free nature. Automotive Industry: They are also used in the automotive industry for creating durable and lightweight parts, such as dashboards, door panels, and interior consoles. Food Industry: Thermoform inserts are used for food packaging, given their ability to be sealed for freshness and their compliance with food safety standards. Retail Display: Retail industries use these inserts for aesthetically pleasing product displays that protect the product while showcasing it effectively. Advantages and Considerations Cost-Effective: Thermoforming is a cost-effective production process, especially for medium to large runs, making thermoform inserts a budget-friendly option. Environmental Considerations: Many thermoform plastics are recyclable, which is a crucial consideration in today’s environmentally conscious market. However, the choice of material and recycling programs available can affect this aspect. Design and Prototyping: The flexibility in design makes thermoform inserts ideal for custom applications. Rapid prototyping is often possible, allowing for quick turnaround from design to production. Limitations: While versatile, there are limitations in terms of the depth and complexity of shapes that can be achieved compared to other forming processes like injection molding. Conclusion Thermoform inserts play a crucial role in various industries due to their unique properties like durability, lightweight nature, and customizability. Their applications range from packaging to automotive parts, showcasing their versatility. When considering thermoform inserts for a project, it’s essential to weigh factors like material properties, environmental impact, and design requirements to ensure they meet the specific needs of the application. With ongoing advancements in materials and thermoforming technology, the potential uses and benefits of thermoform inserts continue to expand. (714)300-0650 request@brownpackaging.com Most Recent Posts: Categories: Corrugated Ecommerce ESD Design Display Flexible Packaging Foam Folding Carton Packaging Plastic Packaging Pouch Printing Protection Retail Rigid Box Thermoform Sustainability Subscribe To Our Newsletter By submitting your information, you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy. Thermoform Insert Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Relevant Posts


