Home » RSC Packaging Cost Efficiency
RSC Packaging Cost Efficiency

RSC boxes are widely used because they balance strength with cost efficiency. But not all RSC boxes are created equal. Buyers have to weigh board grade, flute profile, and design factors to avoid overpaying for unnecessary strength or, worse, underpaying and risking product damage. Understanding these trade-offs ensures that packaging budgets are optimized without compromising protection.
Board Grade and Cost Trade-Offs
- Higher Grades (e.g., 44 ECT)
- Provide greater stacking strength.
- Necessary for heavy products, palletized loads, or export packaging.
- Higher cost due to stronger liners and mediums.
- Lower Grades (e.g., 26–32 ECT)
- Ideal for lightweight products.
- Cost-effective for single-use shipments or direct-to-consumer e-commerce.
- Reduce material cost but lower compression resistance.
Takeaway: Over-specifying board grade adds unnecessary cost. Match strength to actual product weight and stacking requirements.

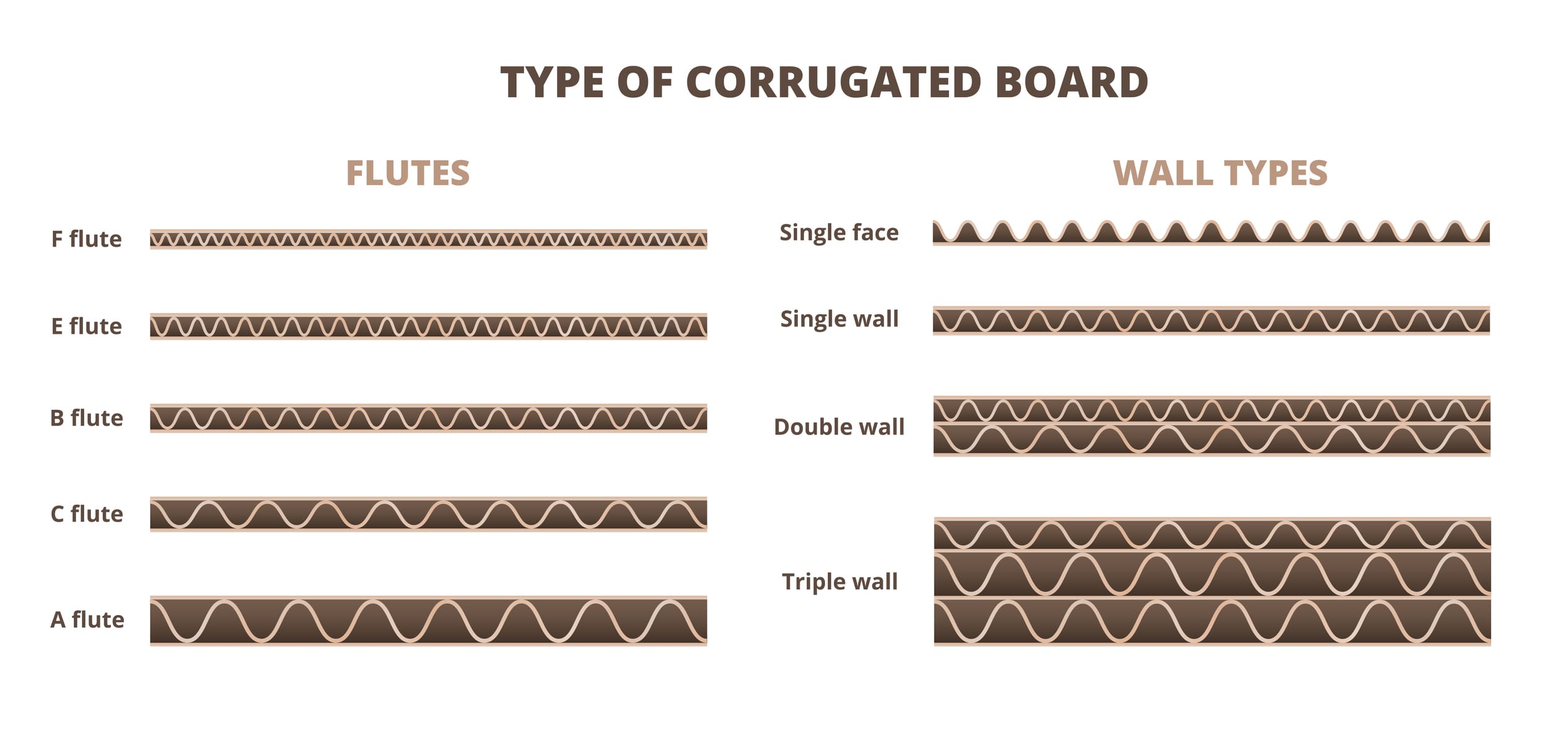
Flute Profiles and Efficiency
- B-Flute: Good balance of cushioning and stacking strength, widely used in RSC.
- C-Flute: Higher cushioning, thicker profile, similar cost per unit.
- E-Flute: Thin profile, less stacking strength but reduces material use and shipping cost for small/light products. Higher cost per unit.
Takeaway: Flute choice affects not only performance but also dimensional weight — a critical factor in freight costs.
Assembly and Material Costs
- Tape and Labor: RSC requires tape or glue for sealing, which adds to per-unit cost at scale.
- Automation: Automated case erectors reduce labor, but box tolerances must be consistent to avoid jams.
- Material Utilization: RSC has one of the most efficient board utilization rates, reducing waste compared to specialty die-cut mailers.

Freight and Storage Efficiency
- Cube Utilization: Right-sizing RSC dimensions reduces dimensional weight charges.
- Palletization: Box dimensions affect how many units fit per pallet — poor fit can increase freight by 10–15%.
- Knock-Down Storage: RSC ships flat, minimizing inbound logistics costs and warehouse space.

Buyer Takeaway
- Use lower board grades for lightweight e-commerce and non-palletized shipments to save cost.
- Reserve higher grades for industrial, heavy-duty, or export applications.
- Right-size your RSCs to minimize dimensional weight surcharges.
- Consider automation compatibility to reduce long-term labor expense.
When optimized, RSC packaging isn’t just cost-efficient — it’s a lever for total supply chain savings.

References
- Fibre Box Association. (2023). Corrugated Cost Optimization. https://www.fibrebox.org
- Association of Independent Corrugated Converters (AICC). (2024). Cost and Efficiency in Corrugated Packaging. https://www.aiccbox.org
- Robertson, G. (2016). Food Packaging: Principles and Practice (3rd ed.). CRC Press.
Product damage during transit is one of the most significant hidden costs in packaging. Each damaged shipment increases returns, erodes customer trust, and raises overall logistics expenses. Full Overlap (FOL)
Moisture and humidity can weaken paperboard fibers, alter structural performance, and compromise print quality. From production to end use, controlling these factors is critical to ensure folding cartons perform as
Flexible pouches rely on laminates to deliver strength, barrier protection, and shelf appeal. A laminate is a structure made by combining multiple film layers—each selected for a specific function. The
Peak season shipping volumes put pressure on every part of the supply chain. For packaging buyers, right-sizing boxes is one of the most effective strategies to reduce freight costs, improve
Home » RSC Packaging Cost Efficiency