Home » How to Engineer Corrugated Packaging for Automation
How to Engineer Corrugated Packaging for Automation
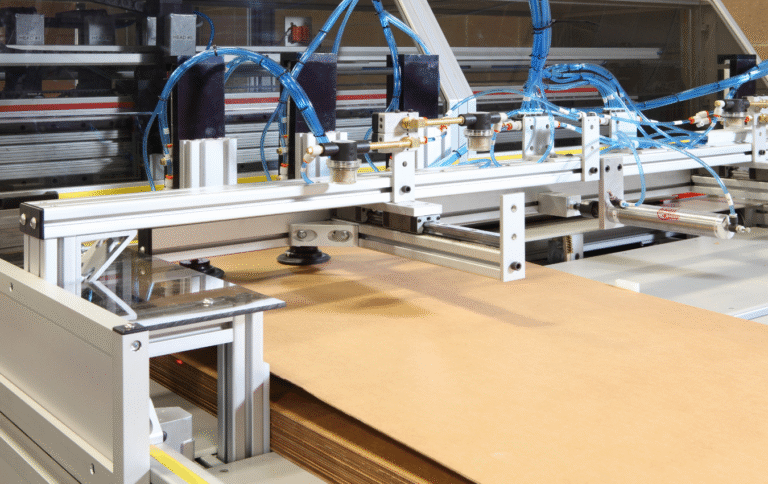

Why Packaging Automation Compatibility Matters
As more fulfillment centers, contract packagers, and manufacturers turn to automation, packaging that isn’t compatible with machinery becomes a costly bottleneck. From misfeeds on case erectors to jams in packing stations, poorly designed corrugated boxes slow down operations, increase error rates, and limit throughput. For high-volume brands and logistics operations, automation-compatible packaging isn’t optional—it’s a core part of the system.
Common Points of Failure with Corrugated in Automation Systems
Automation often fails not because the equipment is faulty, but because the packaging isn’t designed for machine handling. Common issues include:
- Poor dimensional tolerance: If the box flaps don’t align cleanly, case erectors and tapers will jam.
- Low board rigidity: Boxes made from lightweight corrugated collapse during suction or robotic pick-and-place.
- Inconsistent slotting and scoring: Uneven folds confuse sensors or result in skewed box geometry.
- Incompatible closure style: Designs like auto-lock bottoms or complex folds may not be machine-erectable.

Structural Design Principles for Automation Compatibility
✔ Stick to Clean, Repeatable Formats
RSC and FOL boxes with precision scoring are ideal for case erectors and tapers. Avoid overly intricate die cuts or asymmetrical flaps unless they’re downstream of automation.
✔ Use Consistent Die-Lines and Slot Depths
Maintain tight tolerances on slot depth, flap width, and glue tabs. Variability in cutting leads to misfeeds on erectors or case packers.
✔ Right-Size the Box for Consistency
Boxes should hold contents securely with minimal void fill. Automated packout systems are most efficient when the box requires no manual fitting or adjustment.
✔ Add Automation-Friendly Features
If machine-packing is in use, design inserts or partitions that can be preloaded or nested without human intervention. Consistent entry points and fitment are key.

Material Considerations
✔ Choose Higher Rigidity Board Grades
Boards with better stiffness (e.g., 44 ECT or 275#) maintain shape during pick-and-place and resist deformation in automated erecting.
✔ Use Coatings Where Needed
For packaging that passes through friction belts or vacuum suction, a clay-coated or high-slip surface may improve feed reliability.
✔ Avoid Warp
Poor storage conditions or low-quality material lead to box warp, which ruins automation compatibility. Store flat and dry, and use high-quality stock.
Don’t Forget Print Registration
Automation often uses machine vision to scan barcodes or orientation markers. Digital or flexo-printed registration cues must be in consistent locations, with sharp contrast and no ink bleed. Variable data printing can also assist with lot tracking in automated pick-pack systems.

Benefits of Automation-Compatible Corrugated
- Faster throughput with fewer jams or stoppages
- Lower labor costs due to minimal hand correction
- Better reliability in high-speed fulfillment environments
- Scalability when expanding SKUs or entering new distribution channels

Final Thoughts
Corrugated packaging isn’t just a vessel—it’s a mechanical component in an automated system. Brands that optimize their box design, material spec, and print layout for automation reduce errors, increase efficiency, and lower cost per shipment. If you’re designing packaging for automation or reworking a manual process, Brown Packaging can help engineer corrugated solutions that perform in real-world fulfillment lines.
Retail packaging continues to evolve as brands balance sustainability, supply chain performance, and consumer experience. In 2026, buyers face new challenges shaped by material innovation, compliance requirements, and rising consumer
Supplier contracts can make or break a packaging program. Without the right terms, buyers risk price volatility, missed lead times, and inconsistent product quality. In 2026, negotiating smart contracts is
Packaging compliance is no longer optional—it’s a requirement for accessing retail shelves, shipping networks, and international markets. In 2026, buyers must navigate evolving regulations around sustainability, labeling, and testing to
In 2026, sustainability is no longer just a trend—it’s a buyer expectation. Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification has become a key benchmark for responsible packaging, signaling that materials are sourced
Home » How to Engineer Corrugated Packaging for Automation
When it comes to packaging solutions, corrugated boxes offer versatility and protection. Among the common corrugated box styles are the Regular Slotted Container (RSC) box and the Full-Overlap (FOL) box. Each style caters to specific packaging needs, making them suitable for various applications. In this comparative analysis, we will explore the characteristics, use cases, advantages, and considerations of Corrugated RSC Boxes and Full-Overlap (FOL) Boxes to help you determine which is the right choice for your packaging requirements. What is a (RSC) Box? Regular Slotted Container (RSC) boxes are known for their simplicity and efficiency in design and production. They feature four flaps—two on the top and two on the bottom—that meet in the center when closed. RSC boxes are cost-effective and widely used across industries. What is a Full-Overlap (FOL) Box? Full-Overlap (FOL) boxes, in contrast, are designed with flaps that fully overlap when closed, providing added protection and structural integrity. These boxes excel in safeguarding products during transit, making them ideal for items that require extra strength and stability. A Comparative Analysis Design and Closure: Corrugated (RSC) Box: RSC boxes offer a straightforward design, making them easy to assemble and close with tape or adhesive. Closure involves folding the flaps on the top and bottom, taping or gluing to a secure seal. Full-Overlap (FOL) Box: FOL boxes feature overlapping flaps, enhancing structural integrity and security. The flaps provide additional protection and resistance to crushing, making FOL boxes ideal for fragile or heavy items. Protection and Strength: Corrugated (RSC) Box: RSC boxes offer standard protection and are suitable for a wide range of products. While they provide adequate strength, they may not be the best choice for heavy or delicate items. Full-Overlap (FOL) Box: FOL boxes excel in providing enhanced protection and structural integrity. They are ideal for shipping heavy, fragile or valuable items, including electronics, glassware, and machinery. Regular Slotted Container (RSC) Full Overlap (FOL) Versatility: Corrugated (RSC) Box: RSC boxes are versatile and can be used for various products and industries. They are cost-effective and readily available in standard sizes. Full-Overlap (FOL) Box: FOL boxes are versatile as well but are often chosen for specific applications requiring superior protection. They may be slightly more expensive than RSC boxes due to their specialized design. Customization: Corrugated (RSC) Box: RSC boxes can be customized with printed graphics and branding, enhancing their visual appeal. Full-Overlap (FOL) Box: FOL boxes can also be customized with branding and graphics and are often used for premium or high-end products. Cost-Efficiency: Corrugated (RSC) Box: RSC boxes are generally more cost-effective due to their simpler design and ease of production. Full-Overlap (FOL) Box: FOL boxes may come at a slightly higher cost, primarily due to their enhanced protective features. Choosing the Right Box for Your Needs The choice between Corrugated RSC Boxes and Full-Overlap (FOL) Boxes hinges on your specific packaging requirements. Here are some considerations: If you need a cost-effective and versatile solution for standard products, Corrugated RSC Boxes are a practical choice. If you’re shipping fragile or valuable items, heavy machinery, or electronics, Full-Overlap (FOL) Boxes offer superior protection and structural integrity. Customization and branding are possible with both box styles, allowing you to create a unique packaging experience for your customers. If you are interested corrugated boxes like RSC, FOL and other styles, then partner with Brown Packaging today to get started. (714)300-0650 request@brownpackaging.com Most Recent Posts: Categories: Corrugated Ecommerce ESD Design Display Flexible Packaging Foam Folding Carton Packaging Plastic Packaging Pouch Printing Protection Retail Rigid Box Thermoform Sustainability Subscribe To Our Newsletter By submitting your information, you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy. Custom Corrugated Boxes Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Relevant Posts

When it comes to packaging fragile products, the choice of packaging materials and techniques plays a critical role in ensuring your delicate items reach their destination unscathed. Roll End Tuck Top (RETT) boxes offer a versatile solution for safeguarding fragile treasures during transit. In this buyer’s guide, we will delve into the essential steps and strategies for effectively packaging fragile products using RETT boxes, helping you make an informed choice to protect your delicate items. Selecting the Right RETT Box for Fragile Items The first step in packaging fragile products is choosing the appropriate RETT box. As a buyer, consider the following factors: Size: Ensure the box is the right size for your fragile items, allowing for a snug fit without excess space that could lead to movement during transit. Stronger Material: Opt for double-wall RETT boxes to ensure added strength and protection, especially when dealing with particularly fragile items. Internal Packaging: Depending on the fragility of your items, you may need additional internal packaging materials such as bubble wrap, foam inserts, or custom dividers. Wrapping and Cushioning Your Fragile Items Bubble Wrap: As a buyer, it’s essential to procure multiple layers of bubble wrap to wrap your fragile items. Ensure that all surfaces are covered, and pay special attention to any delicate protrusions or corners. Foam Padding: For extra protection, consider purchasing foam padding to wrap around your items. You can choose between cutting foam sheets to size or acquiring pre-cut foam inserts for a snug and cushioned environment. Secure with Tape: Be sure to secure the bubble wrap and foam padding in place using packaging tape. Verify that there are no loose edges or corners that could get caught during transit. Positioning Your Fragile Items in the RETT Box Center Placement: As a buyer, take care to place the wrapped and cushioned fragile items in the center of the RETT box. Ensure that there is a buffer of space between the products and the box walls. Layer of Void Fill: Add a layer of void fill material, such as packing peanuts or air pillows, around the items to further absorb shocks and vibrations during transportation. Sealing and Securing the RETT Box Tuck Top Closure: As a buyer, you should utilize the tuck top closure and cherry locks feature of the RETT box, folding the tuck flaps neatly. This secure closure prevents accidental openings during handling and transport. Sealing Tape: Seal the top of the box using high-quality packaging tape. Make certain that all seams are well-secured and consider using tape to reinforce the corners for added stability. Labeling and Fragile Warning for Buyers Labeling: It is crucial to label the box clearly as “Fragile” on all sides, using bold and easily visible lettering. This notifies handlers to exercise caution when dealing with your fragile items. Orientation Arrows: Buyers may also consider adding orientation arrows to indicate the proper upright position of the box, further reducing the risk of mishandling. Properly Packing Multiple Fragile Items for Buyers When purchasing RETT boxes to package multiple fragile items, buyers should consider these additional tips: Separate and Wrap: Ensure that each fragile item is individually wrapped, cushioned, and separated from the others to prevent contact and potential damage. Layering: Utilize dividers or layers of void fill between the items to create a protective barrier. Staggered Placement: Stagger the placement of items within the box to distribute weight evenly and reduce the risk of breakage. Conclusion for Buyers As a buyer, choosing the right RETT boxes and following these packaging steps and strategies can significantly reduce the risk of damage to your fragile products during transit. By taking these precautions and selecting the appropriate packaging materials, you can have confidence that your delicate items will reach their destination in pristine condition, ensuring customer satisfaction and brand reputation. If you are interested in packaging fragile products with roll end tuck end boxes, then partner with Brown Packaging today to get started. (714)300-0650 request@brownpackaging.com Most Recent Posts: Categories: Corrugated Ecommerce ESD Design Display Flexible Packaging Foam Folding Carton Packaging Plastic Packaging Pouch Printing Protection Retail Rigid Box Thermoform Sustainability Subscribe To Our Newsletter By submitting your information, you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy. Roll End Tuck Top Boxes Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Relevant Posts

Corrugated packaging has been a popular choice for packaging and shipping goods for over a century, and for good reason. The unique structure of corrugated packaging, with its fluted layer between two liners, provides a lightweight yet strong material that can be customized to fit a wide variety of shapes and sizes. However, the environmental benefits of corrugated packaging are often overlooked. With increasing concern over climate change and the impact of waste on the environment, it’s important to consider the sustainability of the materials we use, including packaging. Fortunately, corrugated packaging offers a range of environmental advantages that make it one of the most sustainable packaging materials available today. It’s made from renewable resources, can be easily recycled, and has a relatively low carbon footprint compared to other materials. As consumers become more conscious of their environmental impact, companies are also making an effort to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to sustainable practices. Choosing corrugated packaging is a simple yet effective way to make a positive impact on the environment. By using recyclable and biodegradable materials, companies can reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize their carbon footprint. Overview: Corrugated Packaging, Benefits & Sustainability In this article, we will explore the sustainability benefits of corrugated packaging, including its recyclability, biodegradability, and low carbon footprint. We will also examine how these benefits contribute to a more sustainable future and what steps we can take to promote the use of corrugated packaging. Recyclability Biodegradability Low Carbon Footprint Recyclability Recyclability of corrugated packaging is one of the key reasons it is such a sustainable material. Corrugated packaging is made from paper, which is a renewable resource and can be recycled multiple times. Recycling corrugated packaging is easy and efficient, with the vast majority of materials collected and reused within just a few weeks. In this section, we will explore the different aspects of the recyclability of corrugated packaging, including its collection and sorting, recycling process, and benefits to the environment. Collection and Sorting The first step in the recycling process of corrugated packaging is the collection and sorting of materials. Most municipalities have curbside recycling programs that include corrugated packaging, making it easy for households to recycle. The packaging can also be recycled at local recycling centers or through drop-off programs. Once the materials are collected, they are transported to a recycling facility, where they are sorted and prepared for recycling. Recycling Process The recycling process of corrugated packaging is relatively simple and requires minimal energy compared to other materials. The first step is to remove any contaminants, such as tape or staples, which can be done through a pulping process that separates the fibers from the contaminants. The fibers are then cleaned, screened, and de-inked, and made into new paper products. The entire process can take just a few weeks from the time the packaging is collected to the production of new products. Benefits to the Environment Recycling corrugated packaging has many benefits for the environment. Firstly, it conserves resources, as the paper fibers can be recycled multiple times, reducing the need for new materials. Secondly, it reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, which helps to preserve natural habitats and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Finally, recycling corrugated packaging helps to promote a circular economy, where materials are reused and waste is minimized. Biodegradability Another sustainability advantage of corrugated packaging is its biodegradability. This means that the material can be broken down by natural processes and does not persist in the environment. In this section, we will explore the biodegradability of corrugated packaging, including how it decomposes, the impact on the environment, and the benefits of composting. Decomposition When corrugated packaging is disposed of in a landfill, it decomposes over time and produces methane gas, a potent greenhouse gas. However, the decomposition process of corrugated packaging is significantly faster than other materials such as plastic, which can take hundreds of years to break down. Corrugated packaging is made from paper, which is a natural material that can be broken down by microorganisms. Impact on the Environment When corrugated packaging is recycled, it is diverted from landfills, and methane emissions are reduced. Methane gas is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, so by reducing the amount of corrugated packaging in landfills, we can help mitigate the effects of climate change. Additionally, the biodegradability of corrugated packaging means that it is less likely to persist in the environment and cause harm to wildlife. Composting Corrugated packaging is also an excellent material for composting. It can be shredded and added to a compost pile, where it breaks down quickly and helps to nourish the soil. Composting corrugated packaging also helps to reduce waste and conserve resources. The paper fibers in corrugated packaging provide a good source of carbon for composting, which is essential for creating a balanced compost pile. Benefits of Composting Composting corrugated packaging has many benefits, including reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills, improving soil health, and conserving resources. By adding corrugated packaging to a compost pile, it can help to break down other organic materials, such as food waste, and create a nutrient-rich compost that can be used to grow plants. Low Carbon Footprint The low carbon footprint of corrugated packaging is another important sustainability advantage. The manufacturing process requires less energy compared to other materials, and the packaging is lightweight, which reduces transportation emissions. In this section, we will explore the different aspects of the low carbon footprint of corrugated packaging, including the manufacturing process, transportation emissions, and the impact on the environment. Manufacturing Process The manufacturing process of corrugated packaging requires less energy compared to other materials. The packaging is made from renewable resources, which reduces the reliance on fossil fuels. The process of manufacturing corrugated packaging involves converting wood pulp into paper, which is then formed into the distinctive corrugated structure. The manufacturing process is energy efficient and can be powered by renewable energy sources. Transportation Emissions The lightweight nature of

