Home » Moisture Resistance and Dimensional Stability in Inserts
Moisture Resistance and Dimensional Stability in Inserts
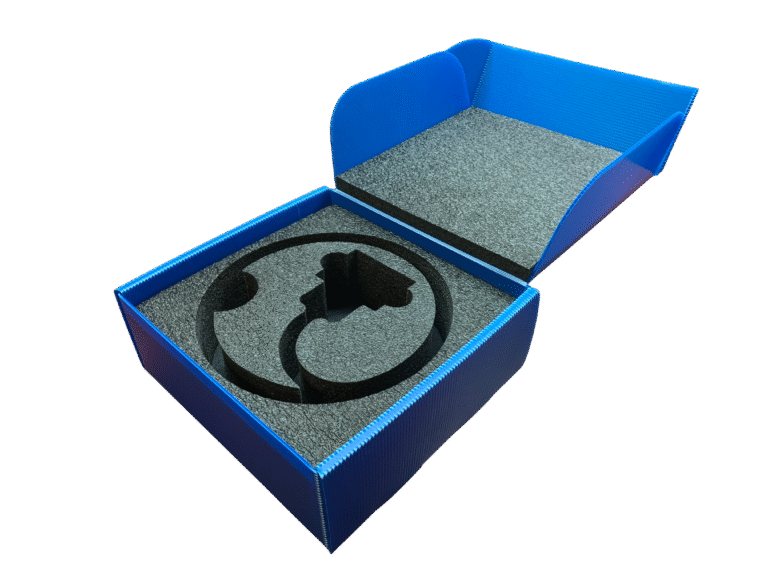
Moisture resistance and dimensional stability are critical performance factors for custom inserts, especially when products are shipped or stored in variable climates. Both foam and corrugated materials react differently to humidity, temperature, and long-term environmental exposure, which can impact product fit, cushioning performance, and structural integrity.
Impact of Humidity on Corrugated Inserts
Corrugated fiberboard is hygroscopic, meaning it naturally absorbs and releases moisture from the surrounding air. This affects compression strength, warping, and dimensional accuracy. In high-humidity environments, standard kraft liners can lose up to 50% of their stacking strength. Coatings, wax treatments, or the use of water-resistant adhesives (meeting TAPPI T-829 standards) can improve performance.
Foam Behavior in Moist Environments
Closed-cell foams, such as polyethylene (PE) and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), resist water absorption and retain their shape under exposure to moisture. Open-cell foams, like polyurethane (PU), are more prone to water ingress, leading to swelling, microbial growth, and loss of cushioning capacity. For products with moisture sensitivity, designers often specify closed-cell foams or integrate vapor-barrier laminations.
Dimensional Stability Under Temperature Shifts
Foam inserts, particularly those with high thermal expansion coefficients, can either loosen or increase compression on the product. Testing under ASTM D4332 (conditioning) ensures the insert maintains performance across the expected temperature range.
Combined Material Designs
When foam and corrugated are combined in a hybrid insert, dimensional stability depends on matching materials with similar expansion and contraction profiles. Mismatched materials can cause warping or delamination over time. Selecting adhesives that remain flexible in varying humidity is critical for long-term stability.
Designing for Real-World Conditions
Inserts should be designed and tested to withstand the extremes of their distribution cycle — from humid seaports to dry inland warehouses. This may involve ISTA 3A/6A testing protocols combined with accelerated aging tests to simulate months of exposure within a compressed timeframe.
References
American Society for Testing and Materials. (2014). ASTM D4332-14: Standard Practice for Conditioning Containers, Packages, or Packaging Components for Testing. https://doi.org/10.1520/D4332-14
International Safe Transit Association. (2018). ISTA 3A Packaged-Products for Parcel Delivery System Shipment 70 kg (150 lb) or Less. https://ista.org/
TAPPI. (2023). T-829 Water Resistance of Paperboard by Wax Treatment. https://www.tappi.org/content/store/shared/T829.html
Soroka, W. (2016). Fundamentals of Packaging Technology (5th ed.). Institute of Packaging Professionals.
Key Compliance Requirements
- Structural standards: Packaging must meet durability and palletization guidelines.
- Labeling accuracy: GS1-compliant barcodes and proper product details.
- Sustainability mandates: FSC certification or recyclability requirements from major retailers.
- Testing protocols: ISTA or ASTM performance tests to validate protection.
Packaging Solutions with Brown Packaging
Brown Packaging partners with companies to design packaging that meets retailer requirements. From GS1 labeling to FSC-certified materials and ISTA-tested corrugated, we help buyers reduce chargebacks and protect retail relationships. Contact us to improve your retail compliance program.
References
GS1. (2024). Global Standards for Packaging and Labeling. Retrieved from https://www.gs1.org
International Safe Transit Association (ISTA). (2023). ISTA Testing Procedures for Transport Packaging. Retrieved from https://ista.org
Forest Stewardship Council (FSC). (2023). FSC Packaging Certification Guidelines. Retrieved from https://fsc.org
Beyond standard drop and compression tests, advanced performance testing provides deeper insight into how folding cartons behave under real-world stresses. These methods help packaging engineers predict failures, validate material changes,
Moisture and humidity can weaken paperboard fibers, alter structural performance, and compromise print quality. From production to end use, controlling these factors is critical to ensure folding cartons perform as
Flexible pouches rely on laminates to deliver strength, barrier protection, and shelf appeal. A laminate is a structure made by combining multiple film layers—each selected for a specific function. The
Peak season shipping volumes put pressure on every part of the supply chain. For packaging buyers, right-sizing boxes is one of the most effective strategies to reduce freight costs, improve
Home » Moisture Resistance and Dimensional Stability in Inserts