Home » Innovation in Sustainable Thermoform Packaging: Current Practices and Future Opportunities
Innovation in Sustainable Thermoform Packaging: Current Practices and Future Opportunities
The packaging industry has been subjected to vast shifts in focus over the past few years. With the growing awareness of sustainability issues and the pressing concern of environmental conservation, businesses have been prioritizing ‘green’ packaging strategies. In this context, sustainable thermoform packaging has emerged as an innovative solution. This blog post delves into the current practices in this domain and the future opportunities it presents.
Understanding Thermoform Packaging
What is Thermoform Packaging?
Thermoforming is a method of packaging that involves heating a plastic sheet to a pliable forming temperature, shaping it to a specific mold, and then trimming it to create a usable product. The resultant packaging is light, strong, and protective. Thermoform packaging is widely used in numerous sectors including food, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and personal care products.
Sustainable Thermoform Packaging Explained
Why Sustainable Thermoform Packaging?
As businesses continue to face increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for eco-friendly products, sustainable thermoform packaging has become a viable and attractive alternative. It addresses the core need of durability and product protection, while also reducing the ecological footprint.
Materials in Sustainable Thermoform Packaging
The heart of sustainable thermoform packaging lies in the materials used. These range from bio-based plastics, recycled post-consumer plastic, to other eco-friendly materials.
- Bio-based plastics: These are derived from renewable sources such as corn starch, sugar cane, and other plant-based materials. These bioplastics are designed to biodegrade under specific conditions and are often used in food and beverage packaging.
- Recycled post-consumer plastic: These materials, recovered from consumer waste streams, are cleaned, processed, and recycled into new packaging materials. The use of post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastic can significantly reduce the need for virgin plastic production.
Innovations in Sustainable Thermoform Packaging
Design Innovations
Advancements in design have led to more efficient and sustainable thermoform packaging options. For example, packaging designs are becoming more minimalistic, reducing material usage while maintaining product protection. Innovation also extends to the use of mold technologies that can accurately form complex shapes, improving material efficiency.
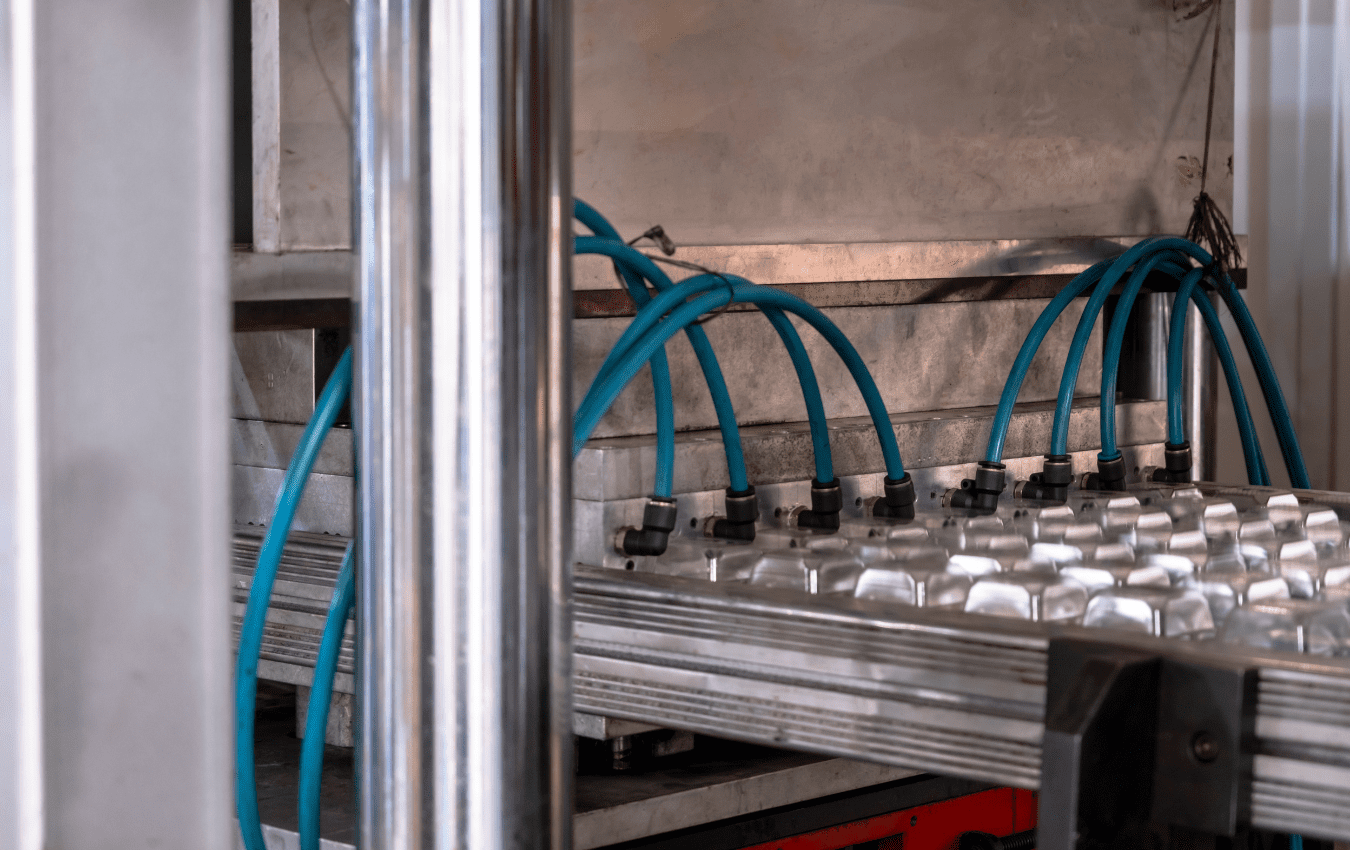
Technology Innovations
New technologies are also playing a vital role in enhancing the sustainability of thermoform packaging. Advanced thermoforming machines are more energy-efficient, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the packaging process. In addition, techniques like vacuum thermoforming and pressure forming are enabling the creation of lighter, yet durable, packaging solutions.
The Future of Sustainable Thermoform Packaging
Opportunities and Challenges
The future holds great promise for sustainable thermoform packaging, but also poses significant challenges. The main opportunity lies in innovation, particularly in the areas of material science, design, and technology.
However, one of the significant challenges will be to scale up the use of these innovations while managing costs. Furthermore, while bio-based plastics and recycled materials offer great promise, issues surrounding their compostability and recyclability need further exploration and solutions.
Potential Areas for Growth
Sectors like food, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals already heavily use thermoform packaging. However, sectors like electronics and automotive components present a vast untapped market, as these industries strive to reduce their environmental impact.
Policy and Regulation
With governments globally increasingly focusing on sustainability, future policy and regulations are expected to be more favorable towards sustainable packaging. Tax benefits, subsidies, or other incentives could further drive the adoption of sustainable thermoform packaging.
Consumer Awareness and Demand
Consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products will continue to be a major driver for the growth of sustainable thermoform packaging. As more consumers understand the benefits of sustainable packaging, businesses will be incentivized to adopt these practices.
If you are interested in thermoform packaging, then partner with Brown Packaging today.
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are valued for their durability, with overlapping flaps that add protection on the top and bottom panels. But the strength
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are engineered for strength. Unlike a Regular Slotted Container (RSC), the major flaps on an FOL extend the full width
Product damage during transit is one of the most significant hidden costs in packaging. Each damaged shipment increases returns, erodes customer trust, and raises overall
Moisture and humidity can weaken paperboard fibers, alter structural performance, and compromise print quality. From production to end use, controlling these factors is critical to
Flexible pouches rely on laminates to deliver strength, barrier protection, and shelf appeal. A laminate is a structure made by combining multiple film layers—each selected
Peak season shipping volumes put pressure on every part of the supply chain. For packaging buyers, right-sizing boxes is one of the most effective strategies
Home » Innovation in Sustainable Thermoform Packaging: Current Practices and Future Opportunities

In the world of packaging, different products require different packaging solutions. With myriad options available today, companies can be selective about which suits their needs

Effective packaging plays a crucial role in product presentation and protection across various industries. Among the many packaging options available, blister packaging stands out as

Polyethylene terephthalate, commonly abbreviated, stands out in the packaging industry for its versatility and environmental friendliness. Recognized as the most widely recycled plastic worldwide, this