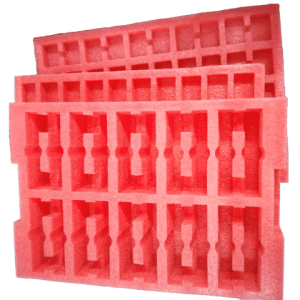
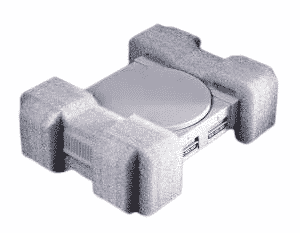
The Different Types Of Packaging Foam
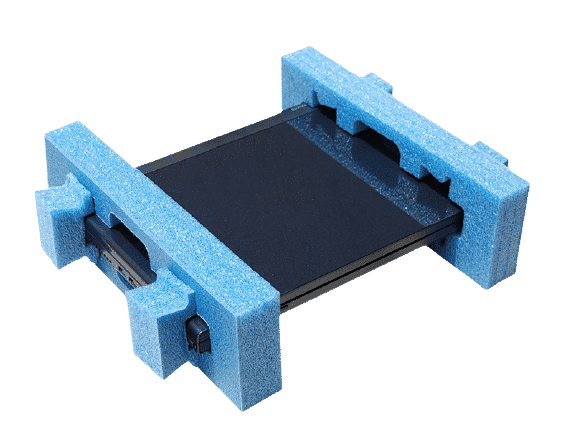
Packaging foam is essential for protecting products against shocks, vibrations, and other potential damages during transportation and storage. Understanding the different types of packaging foam available can help you choose the most suitable option based on your specific needs. This guide covers a variety of foam types, including the primary options—polyurethane, polyethylene, and expanded polystyrene (EPS)—and introduces additional varieties, each with unique properties and applications.
Overview of Major Foam Types
Polyethylene Foam (PE)
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell foam known for its durability and versatility. It’s made by heating and molding polymer compounds into millions of tiny bubbles, all sealed off from each other.
Benefits:
- Chemical and Moisture Resistance: Highly resistant to chemicals and moisture.
- Durability: Offers excellent vibration and compression protection.
- Versatility: Customizable in multiple densities and colors with additives like fire retardants and anti-static agents.
- Fabrication Flexibility: Easily processed and fabricated into various shapes.
Disadvantages:
- Environmental Impact: Challenges in recycling and potential toxicity when burned.
- Cost: More time-consuming and costly to fabricate compared to other materials.
Applications:
- Used in industries such as electronics, medical, and construction for end caps, box liners, and protective blocks.
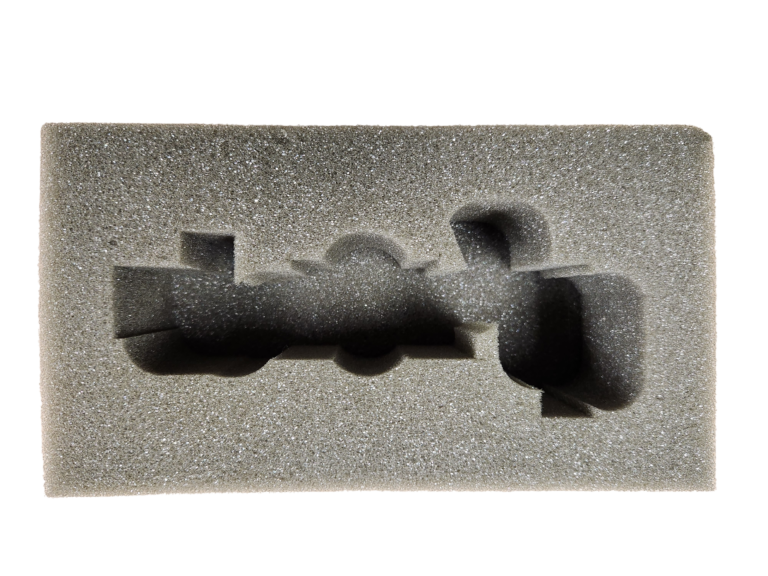

Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is an open-cell foam that is flexible and known for its excellent cushioning properties.
Benefits:
- Cushioning Properties: Superior for protecting delicate items.
- Lightweight: Reduces shipping costs.
- Customization: Available in multiple colors and easily laminated.
- Thermal Insulation: Suitable for temperature-sensitive shipments.
Disadvantages:
- Flammability: Emits toxic gases when burned.
- Odor: May not be suitable for odor-sensitive applications.
- Durability: Shorter shelf-life than closed-cell foams.
Applications:
- Commonly used in protective packaging for electronics, medical devices, and specialty packaging designs.
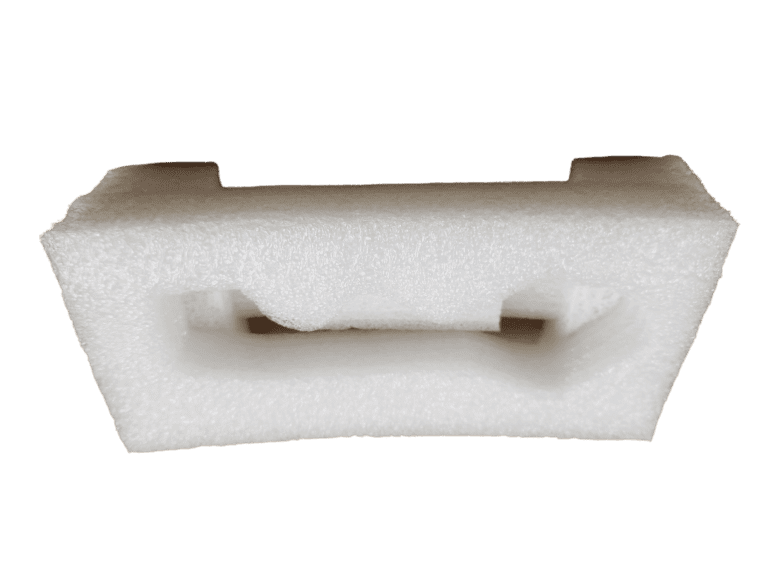

Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
EPS is a lightweight, molded, closed-cell foam, often referred to by its brand name, Styrofoam.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Economical for various applications.
- Lightweight and Strong: Provides excellent protection without significant weight.
- Insulation: Good thermal resistance.
- Moisture Resistance: Does not absorb water, ideal for humid environments.
Disadvantages:
- Environmental Concerns: Difficult to recycle and not eco-friendly.
- Durability: Brittle and degrades under UV exposure.
Applications:
- Widely used in shipping containers for food and medical supplies and protective packaging.
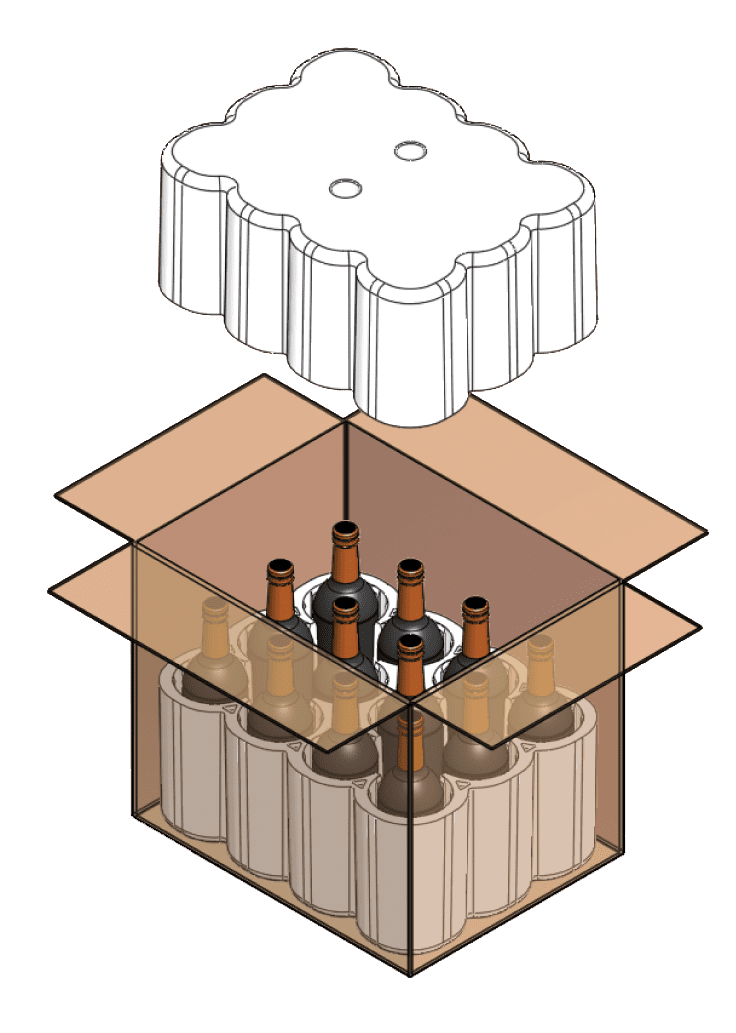
Additional Types of Packaging Foam
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
EVA foam is known for its rubber-like softness and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring a smooth and soft texture.
Benefits:
- Shock Absorption: Excellent for sports equipment and luxury packaging.
- Water Resistance: Does not absorb water, enhancing its durability.
- Chemical Resistance: Resists oils and greases, suitable for industrial applications.
Applications:
- Commonly used for padding in equipment, sports gear, and high-end retail packaging.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam
This type of foam offers superior durability and is ideal for requiring fine, aesthetic finishes.
Benefits:
- Smooth Surface: Provides a clean, professional look.
- High Durability: Resistant to tearing and punctures.
- Thermal Stability: Maintains properties over a wide temperature range.
Applications:
- Used for medical devices, automotive interiors, and cases for delicate instruments.
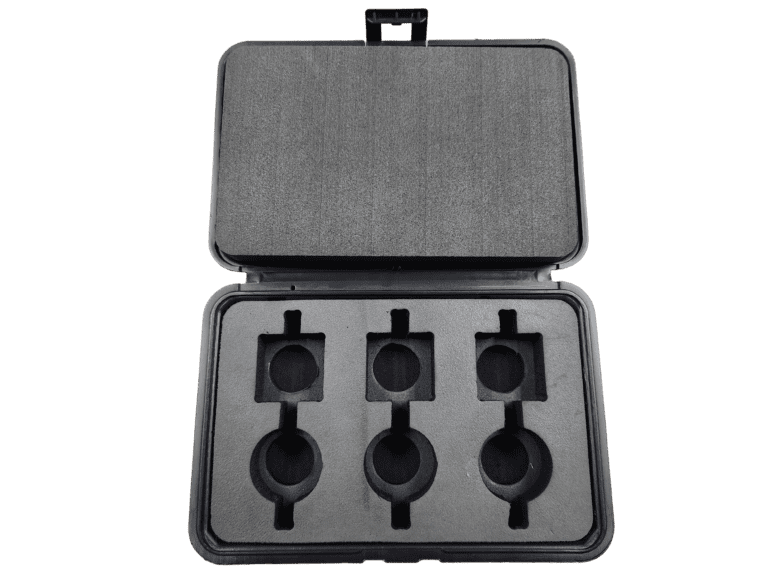

Conclusion: Different Types of Packaging Foam
The variety of packaging foams available offers businesses a wide range of options to protect and enhance their products. From the versatile polyethylene and cushioning polyurethane to the economical EPS and specialized foams like EVA and cross-linked polyethylene, each type provides unique benefits suited to different packaging needs. Understanding these options will help you select the best foam type for your specific product protection, branding, and sustainability goals.
If you are interested in exploring custom packaging foam solutions tailored to your products, consider partnering with a specialist like Brown Packaging to navigate the selection process and optimize your packaging strategy effectively.
The packaging industry has spent decades chasing “more.” More layers, more coatings, more colors — all to create perceived value. But in 2026, the smartest
Packaging decisions should never be based on design alone. Without proper testing, even well-engineered boxes can fail under real-world conditions—leading to product damage, returns, and
The Regular Slotted Container (RSC) is the most widely used corrugated box style, valued for its efficiency and versatility. However, it isn’t always the right
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are valued for their durability, with overlapping flaps that add protection on the top and bottom panels. But the strength
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are engineered for strength. Unlike a Regular Slotted Container (RSC), the major flaps on an FOL extend the full width
Product damage during transit is one of the most significant hidden costs in packaging. Each damaged shipment increases returns, erodes customer trust, and raises overall

In packaging, foam isn’t just about initial protection — it’s about maintaining performance over the entire shipping or storage cycle. Compression set and recovery characteristics

Choosing the right foam density isn’t about “soft” versus “hard” — it’s about controlling shock transmission and matching the foam’s cushioning curve to the product’s
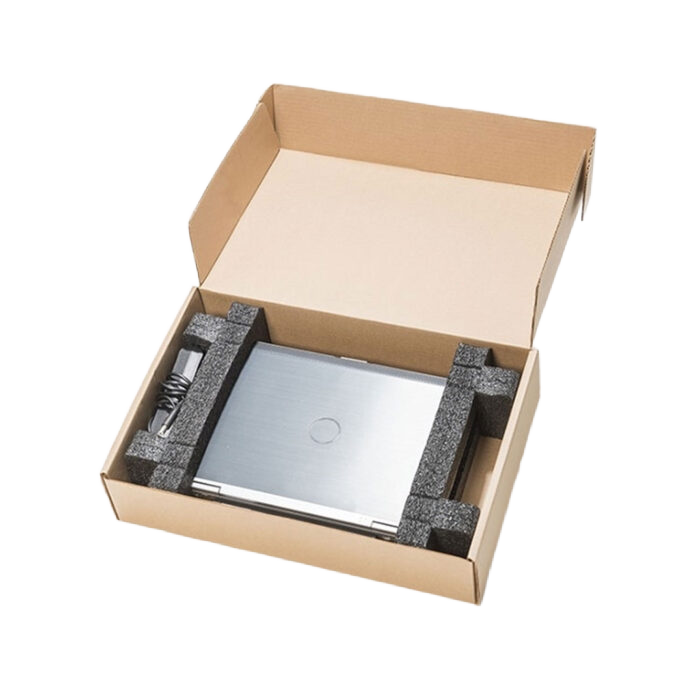

Foam-in-corrugated hybrid inserts combine the cushioning properties of foam with the structural rigidity of corrugated board, creating a packaging solution that is both protective and