Home » Strategies to Protect Packaging Against Temperature Fluctuations
Strategies to Protect Packaging Against Temperature Fluctuations

Temperature fluctuations can have a detrimental effect on your products and packaging. Whether your goods are sensitive to extreme heat or cold, maintaining the right temperature during storage and transportation is essential. In this blog, we’ll explore various strategies and best practices to help you protect your packaging against temperature fluctuations effectively.
Understanding the Risks
Before we delve into protective measures, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks associated with temperature fluctuations:
- Product Quality: Fluctuating temperatures can alter the quality, texture, and taste of products, rendering them unsellable or unsafe for consumption.
- Chemical Reactions: Some products, particularly chemicals and pharmaceuticals, can undergo chemical reactions when exposed to temperature extremes, resulting in changes in composition or efficacy.
- Packaging Integrity: Extreme temperatures can weaken packaging materials, making them more susceptible to tears, punctures, or structural damage.

Protective Measures
To safeguard your packaging against temperature fluctuations, consider implementing the following protective measures:
Temperature-Controlled Packaging:
Use temperature-controlled packaging solutions, such as insulated boxes, coolers, or heated containers, depending on the specific temperature requirements of your products.
Insulated Packaging Materials:
Choose packaging materials with insulating properties. Foam, bubble wrap, or insulated liners can help maintain stable temperatures within the package.
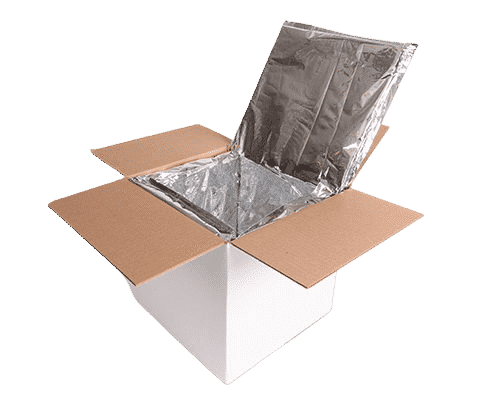

Phase-Change Materials:
Incorporate phase-change materials or gel packs into your packaging. These materials can absorb or release heat to help regulate the temperature inside the package.
Seal Integrity:
Ensure that packaging seals are strong and airtight. Regular quality control checks should verify that no gaps or defects exist in the sealing process to prevent temperature infiltration.
Packaging Design Considerations:
Design packaging with temperature resistance in mind. Use materials that can withstand temperature extremes, and consider multi-layer structures for added insulation.

Quality Testing:
Conduct rigorous testing to verify the effectiveness of your packaging in maintaining temperature stability. Use temperature testing chambers to simulate real-world conditions.
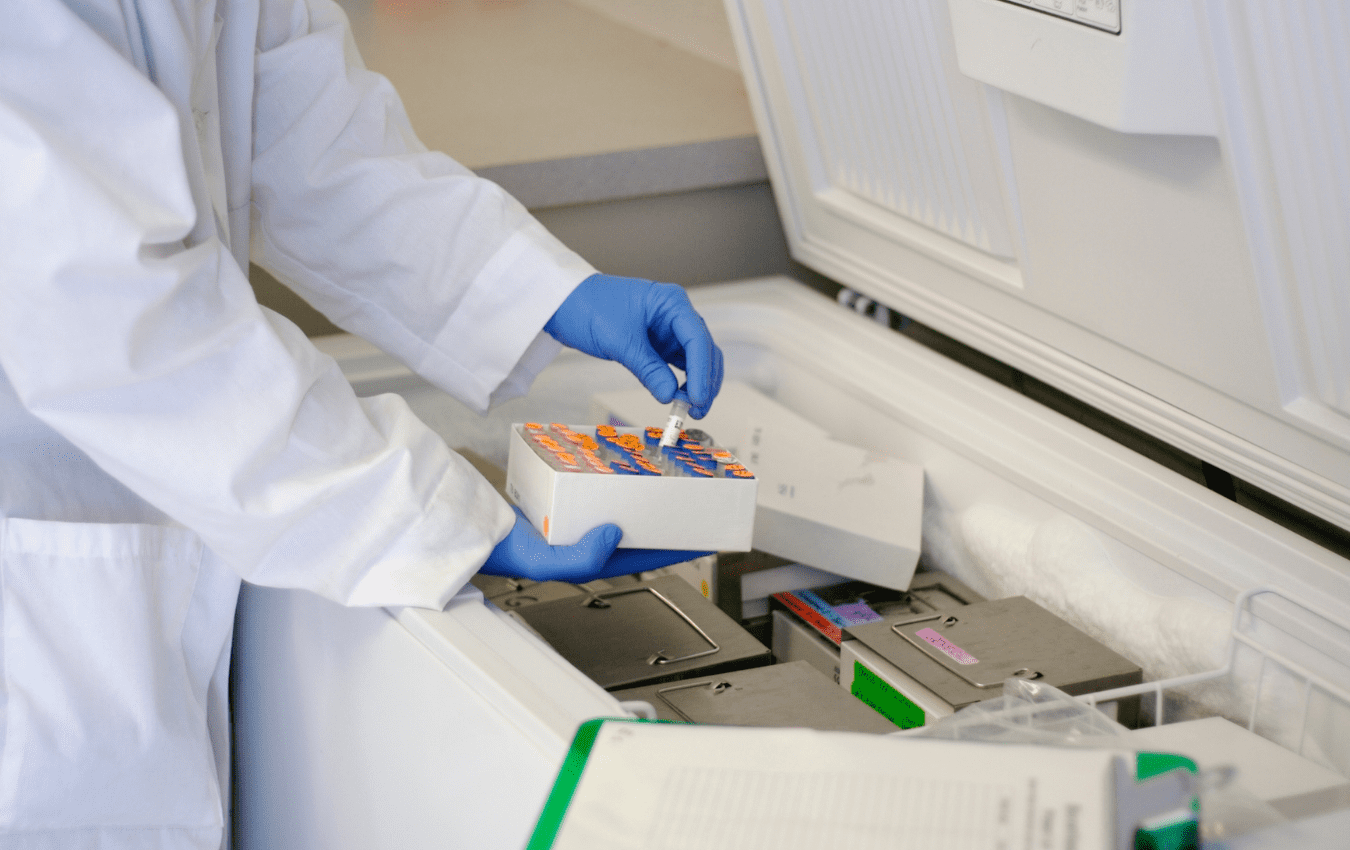
Temperature Monitoring Devices:
Incorporate temperature monitoring devices, such as data loggers or indicators, into your packaging. These devices record temperature data during transit, providing insight into temperature fluctuations.
Controlled Storage Facilities:
Store products in temperature-controlled environments before and after packaging. Warehouses and storage areas should be equipped with adequate ventilation, heating, and cooling systems.
Shipping Route Planning:
Select shipping routes and carriers that prioritize temperature control and offer refrigerated or climate-controlled transportation options.
Regulatory Compliance:
Adhere to industry-specific and regulatory standards for temperature-sensitive products. Compliance ensures that your products meet safety and quality requirements.

Vigilance and Continuous Improvement
Protecting your packaging against temperature fluctuations is an ongoing effort. Continuously assess your packaging solutions and gather feedback from transportation partners to identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments to enhance temperature resilience and ensure that your products arrive at their destination in optimal condition.
By implementing these strategies and maintaining a proactive approach to packaging protection, you can significantly reduce the risk of temperature-related damage to your products, enhance their overall quality and safety, and meet the specific temperature requirements of your industry.
If you are interested in protection against temperature fluctuations for your packaging, then partner with Brown Packaging today to get started.
The packaging industry has spent decades chasing “more.” More layers, more coatings, more colors — all to create perceived value. But in 2026, the smartest brands are realizing that doing
Packaging decisions should never be based on design alone. Without proper testing, even well-engineered boxes can fail under real-world conditions—leading to product damage, returns, and wasted costs. By testing packaging
The Regular Slotted Container (RSC) is the most widely used corrugated box style, valued for its efficiency and versatility. However, it isn’t always the right choice. Certain products, supply chain
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are valued for their durability, with overlapping flaps that add protection on the top and bottom panels. But the strength of an FOL container depends
Home » Strategies to Protect Packaging Against Temperature Fluctuations