Home » Polyethylene vs. Polyurethane Foam for Packaging
Polyethylene vs. Polyurethane Foam for Packaging

When selecting foam materials for packaging, polyethylene foam (PE) and polyurethane foam (PU) are two popular choices. While both offer protection and cushioning, their properties, applications, and advantages differ significantly. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision for your specific packaging needs.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
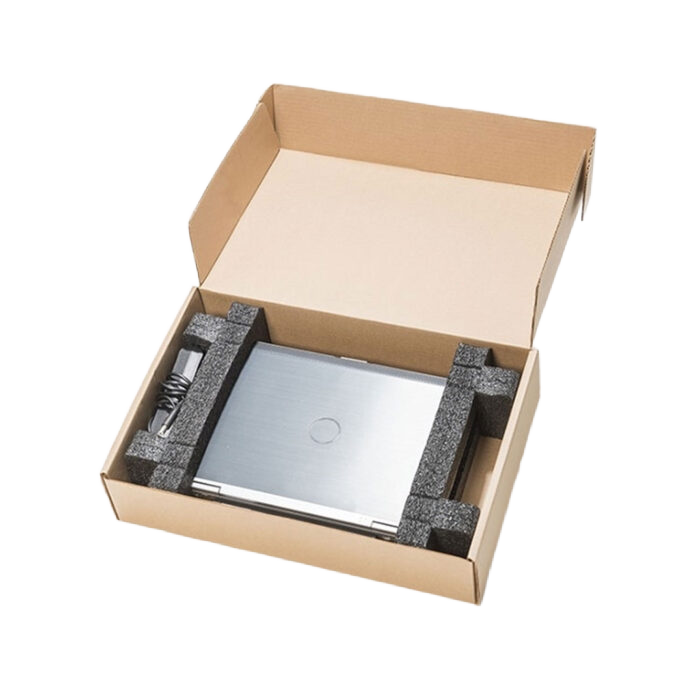
Polyethylene foam, or PE foam, is a lightweight and cost-effective material known for its flexibility and good insulation properties. Commonly used in packaging, PE foam provides cushioning, void fill, and surface protection for delicate items.
Common Applications:
- Cushioning fragile items: Electronics, glassware, and delicate goods during shipping.
- Surface protection: Preventing scratches on furniture or appliances during storage or transport.
- Void fill: Filling empty spaces in packages to secure products.
Customizations:
- Flame retardants for fire resistance.
- UV stabilizers to prevent degradation from sunlight exposure.
- Anti-static agents to protect sensitive electronic components.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam, or PU foam, is a more durable and versatile material compared to polyethylene foam. It offers excellent insulation, water resistance, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
Common Applications:
- Industrial packaging: Protecting heavy equipment, automotive parts, and machinery.
- Impact protection: Absorbing vibration and shock during transportation.
- Insulation: Used in construction for thermal and sound insulation.
Customizations:
- Colorants for aesthetic purposes.
- Flame retardants for enhanced safety.
- UV stabilizers for durability under sun exposure.
Key Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Polyethylene Foam:
- Cost-Effective: Lower cost compared to PU foam.
- Lightweight: Ideal for reducing shipping weight.
- Flexible: Easily cut or shaped for various packaging needs.
- Good Insulation: Protects against temperature changes.
Disadvantages of Polyethylene Foam:
- Lower Durability: Less resistant to water, chemicals, and impact.
- UV Degradation: Can deteriorate over time with sunlight exposure.
Advantages of Polyurethane Foam:
- Durability: Withstands repeated use and tough conditions.
- Resistance: Protects against water, chemicals, and impact.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Shock Absorption: Superior protection for heavier items.
Disadvantages of Polyurethane Foam:
- Higher Cost: More expensive than PE foam.
- Density: Heavier and less flexible, limiting its use in certain applications.
Sustainability Considerations
Neither polyethylene nor polyurethane foam is biodegradable. Both materials take hundreds of years to decompose and can contribute to environmental pollution if not properly disposed of. However, polyethylene foam is more commonly recycled due to its lower density and easier handling during the recycling process.
How to Choose Between PE and PU Foam
Selecting the right foam depends on your specific needs:
- Cost Sensitivity:
Choose polyethylene foam if budget constraints are a primary concern. - Durability Needs:
Use polyurethane foam for applications requiring resistance to water, chemicals, or rough handling. - Product Weight:
For lightweight items, PE foam is ideal. For heavy or fragile items, PU foam provides superior protection. - Environmental Exposure:
Consider PE foam for indoor storage or applications with minimal exposure to moisture or chemicals. Opt for PU foam for outdoor or industrial use.
Conclusion
Both polyethylene and polyurethane foams have unique strengths, making them suitable for different packaging needs. By understanding the properties and applications of each material, you can choose the one that best meets your requirements.
If you’re looking for customized foam solutions, contact Brown Packaging today to explore our range of PE and PU foam options tailored to your needs.
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are valued for their durability, with overlapping flaps that add protection on the top and bottom panels. But the strength of an FOL container depends
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are engineered for strength. Unlike a Regular Slotted Container (RSC), the major flaps on an FOL extend the full width of the box and overlap
Product damage during transit is one of the most significant hidden costs in packaging. Each damaged shipment increases returns, erodes customer trust, and raises overall logistics expenses. Full Overlap (FOL)
Moisture and humidity can weaken paperboard fibers, alter structural performance, and compromise print quality. From production to end use, controlling these factors is critical to ensure folding cartons perform as
Home » Polyethylene vs. Polyurethane Foam for Packaging