Home » How To Choose The Right Stretch Film for Your Application
How To Choose The Right Stretch Film for Your Application

Selecting the right stretch film is essential for ensuring the stability, safety, and integrity of your products during storage and transit. Stretch film plays a crucial role in protecting products on pallets, minimizing damage, and reducing losses. Understanding the basics of stretch film and the specific needs of your application is key to making the right choice.
To select the right stretch film for your application, you must consider the following factors:
- Load Type
- The Type of Product You Are Shipping
- Application Methods
- Cost
Detailed Considerations When Selecting Stretch Film
Load Type
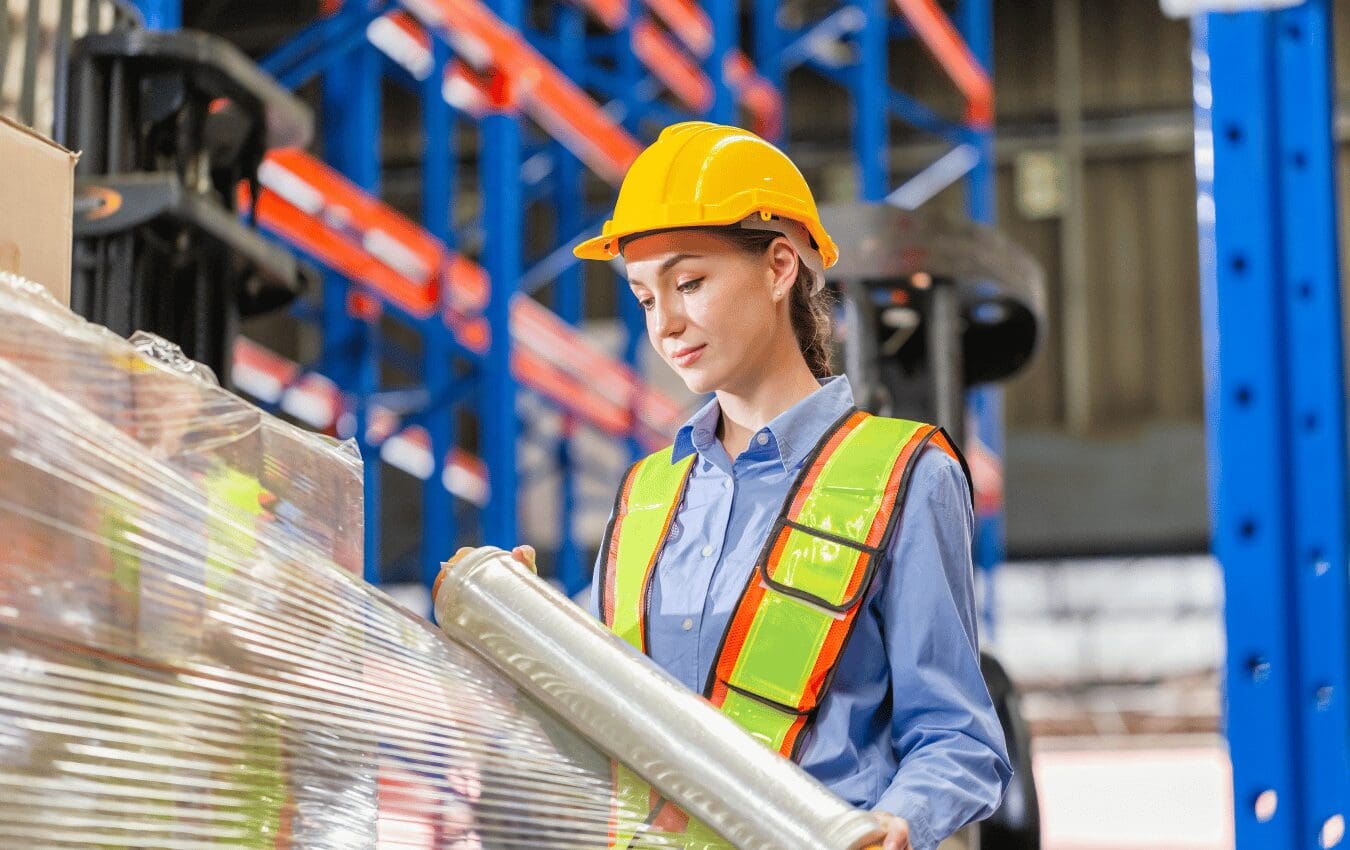
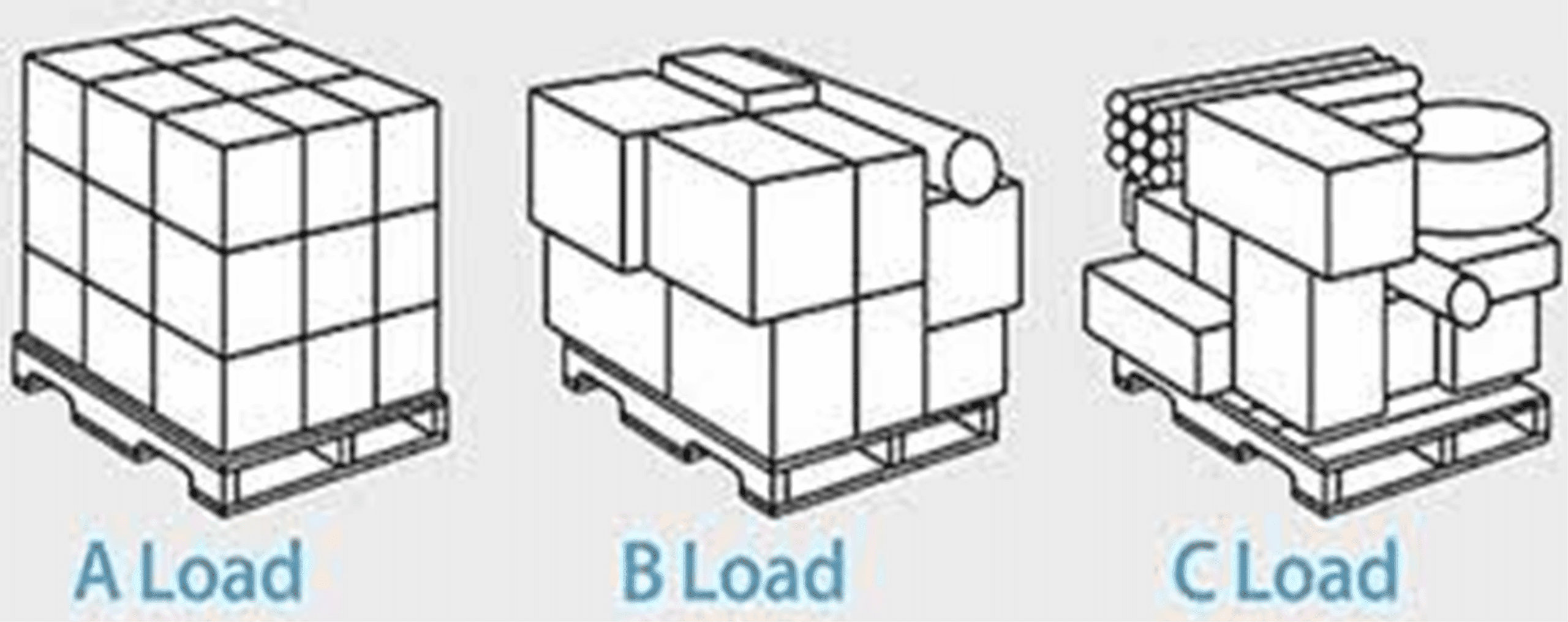
Understanding the type of load you are securing is crucial in selecting the appropriate stretch film. Loads can be categorized into three main types:
- Type A Loads: Uniform loads with straight edges that are similar in shape to the pallet. These loads are easier to wrap and are less prone to puncturing the film.
- Type B Loads: Loads with some irregular shapes or slightly overhanging edges which can challenge the film’s integrity and require more durable film to prevent tears.
- Type C Loads: Highly irregular loads with sharp edges or unstable stacking that pose the highest risk for puncturing and tearing. These require the strongest, most resilient films.
Product Type and Weight
The type of product and its weight influence the choice of stretch film:
- Light Loads: For products like tissues or paper goods, a lighter gauge film can suffice.
- Medium Loads: Products such as canned goods that weigh more but aren’t excessively heavy might need a medium gauge film for better performance.
- Heavy Loads: For items like bricks or chemicals, a heavy-duty film is necessary to accommodate the increased weight and potential shifting within the load.
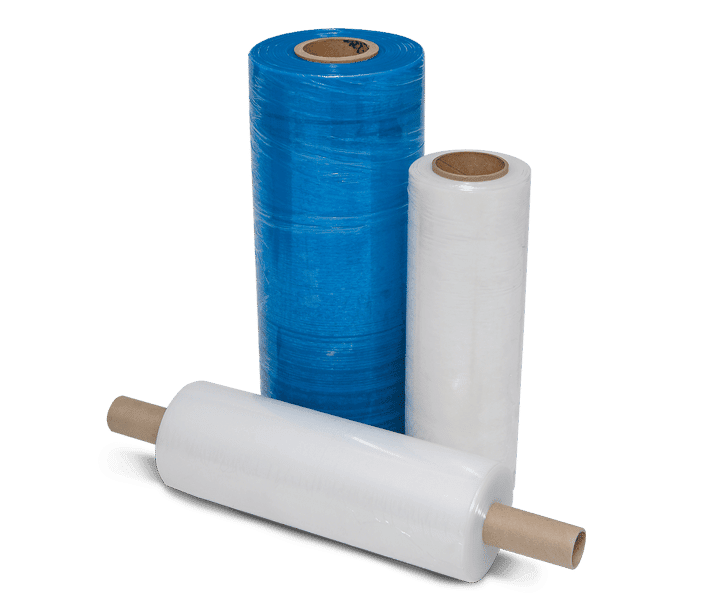
Application Methods
The method of application significantly affects the type of stretch film needed:
- Hand Rolls: Best for low-volume packaging operations or where machinery is not feasible. Hand rolls are lighter and more manageable for manual application.
- Machine Rolls: Ideal for high-volume environments where machines can apply the film much faster and more consistently than manual applications.

Cost Considerations
Budget is always a concern, but balancing cost with quality is key:
- Economic Films: Typically thinner and less durable, suitable for light, uniform loads that require basic containment.
- Premium Films: More expensive, these films offer better stretch, durability, and puncture resistance for challenging load types.
Special Product Requirements and Additives
Depending on the specific needs of the products being shipped, different additives in stretch films can provide necessary protection:
- UV Protection: Essential for products exposed to sunlight during storage or transit to prevent degradation.
- Anti-Static Films: Crucial for electronic products to prevent static discharge during handling.
- Colored Films: Useful for coding shipments by destination or product type, enhancing organization and handling efficiency.


Sustainability Options
Consider environmentally friendly films that reduce the impact on the environment without compromising on quality or performance:
- Recycled Content Films: Made from post-consumer or post-industrial recycled materials.
- Biodegradable Films: Designed to break down more quickly than traditional plastics, reducing waste in landfills.
Summary: Making the Right Stretch Film Choice
To effectively select the right stretch film, you must analyze the load type and product characteristics to determine the film’s required strength and resistance. Consider the operational context, such as the volume of wrapping needed and whether it will be done manually or with machines. Balance your budget with the need for film performance to avoid over-spending or under-protecting your products. Evaluate any special requirements such as UV protection, anti-static properties, or color coding. Opt for sustainable options where possible to align with environmental goals.
By thoroughly assessing these factors, you can choose a stretch film that not only meets your logistical requirements but also enhances the security and integrity of your shipments. For tailored solutions that match your specific needs, consulting with a professional packaging supplier like Brown Packaging can provide you with the expertise and product range to ensure optimal protection and performance.
The packaging industry has spent decades chasing “more.” More layers, more coatings, more colors — all to create perceived value. But in 2026, the smartest
Packaging decisions should never be based on design alone. Without proper testing, even well-engineered boxes can fail under real-world conditions—leading to product damage, returns, and
The Regular Slotted Container (RSC) is the most widely used corrugated box style, valued for its efficiency and versatility. However, it isn’t always the right
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are valued for their durability, with overlapping flaps that add protection on the top and bottom panels. But the strength
Full Overlap (FOL) corrugated boxes are engineered for strength. Unlike a Regular Slotted Container (RSC), the major flaps on an FOL extend the full width
Product damage during transit is one of the most significant hidden costs in packaging. Each damaged shipment increases returns, erodes customer trust, and raises overall
Home » How To Choose The Right Stretch Film for Your Application
Packaging plays a crucial role in protecting products during transit and storage. Among the various materials used for packaging, polyethylene foam stands out as an

In an increasingly competitive and environmentally conscious world, protective packaging has become an essential component of product manufacturing and delivery. The demand for efficient and

In the current competitive retail landscape, the packaging of a product plays an increasingly significant role in customer decision-making. Brands are progressively realizing the power


