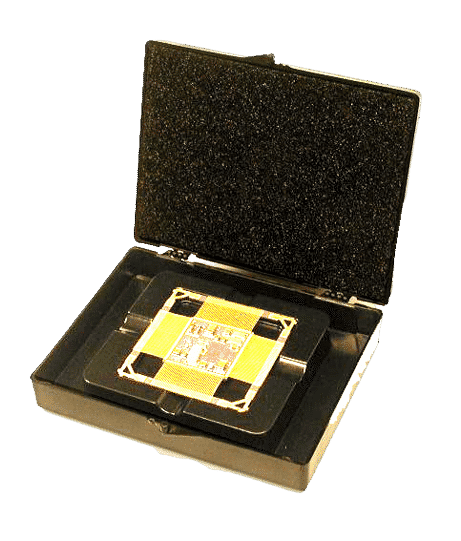
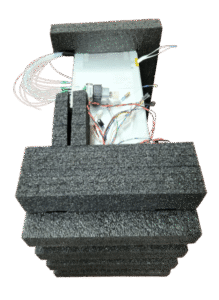
Custom Packaging
We offer a wide selection of fully customizable packaging products to address any packaging purpose. Customize your packaging product with your logo, brand colors, product information, design, features, and more. If you are unsure on what type of packaging you will need, then contact us for an expert consultation.
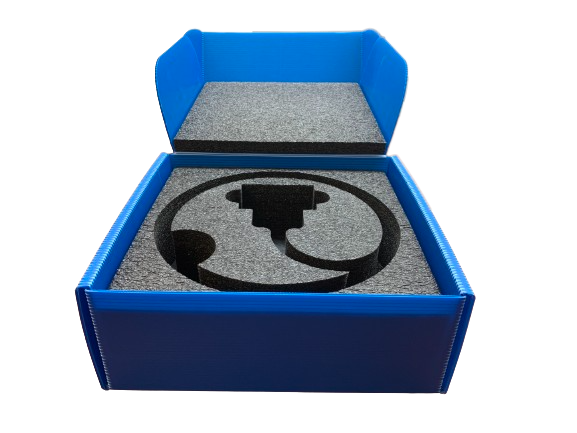




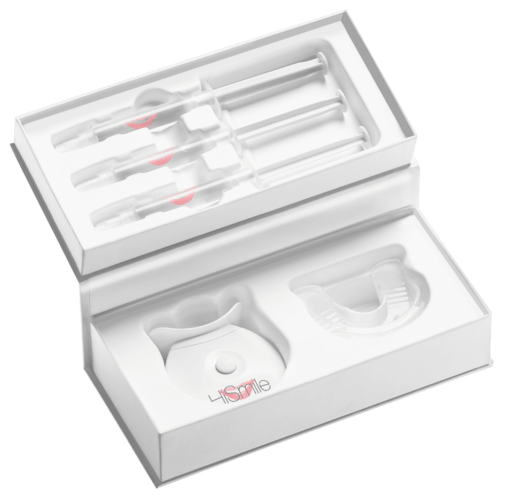
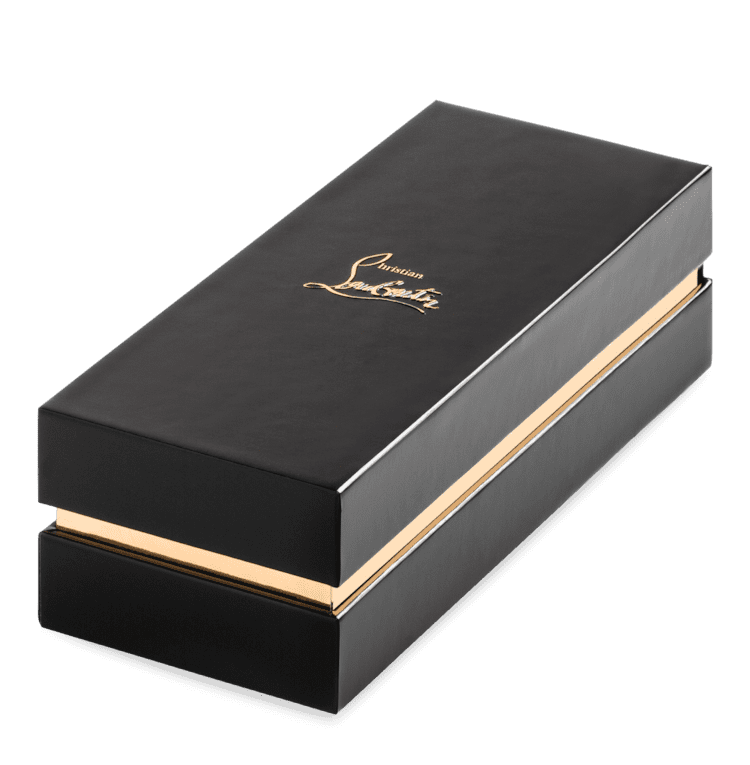
Custom packaging is tailored specifically to fit a brand’s unique product requirements, unlike stock packaging, which is pre-made and generic. Custom options allow for precise sizing, materials, and design choices, offering enhanced protection, presentation, and improved efficiency. This personalization makes custom packaging ideal for businesses looking to stand out and create a cohesive brand identity.
At Brown Packaging, our custom packaging solutions are structurally designed to optimize protection, material usage, and sustainability, tailored to meet specific product needs across various applications. We incorporate graphics to reinforce brand identity, ensuring that each package not only protects but also represents your brand effectively. With a focus on durability and functionality, our packaging ensures secure handling for shipping, retail, or storage while supporting sustainability goals.
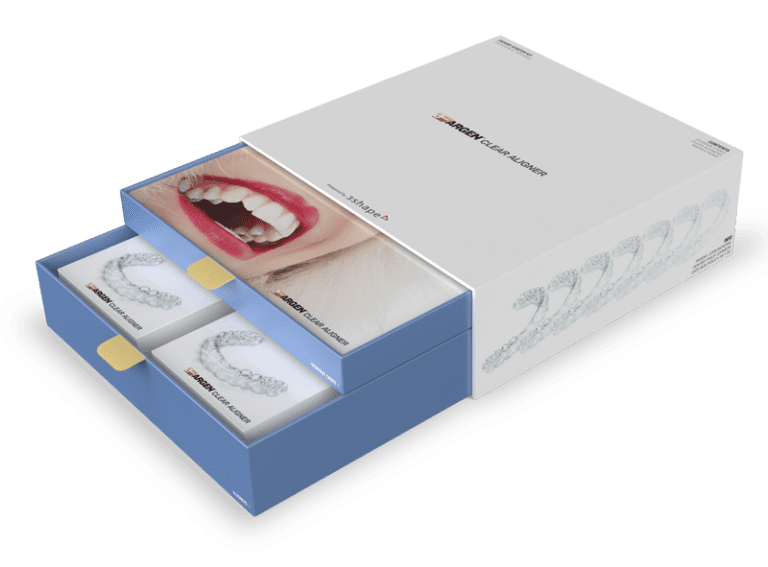
Custom Packaging Products
We offer a variety of custom packaging products and solutions to meet all your packaging needs in one place. You’ll work directly with a dedicated project specialist to customize your package according to your specifications, including branding, features, and design.










If you need any assistance with your packaging or have a question, then contact us directly at request@brownpackaging.com or (714)300-0650. Learn more about custom packaging by reading our blog posts on new and trending topics.